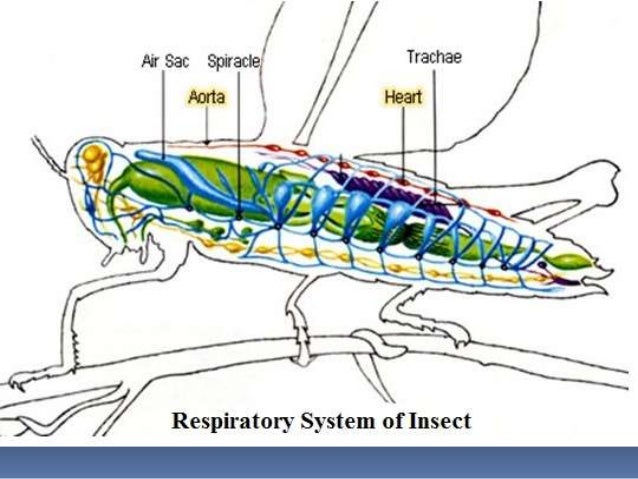
Grasshoppers have eighteen spiracles, nine to a side. On each side, a longitudinal trunk (the primary trachea) connects all ipsilateral spiracles. Anastomoses connect the two sides of the system.
GASEOUS EXCHANGE BY MEANS OF TRACHEOLESMIS EFFICIENT IN SMALL INSECT
Gill filaments are the red, fleshy part of the gills; they take oxygen into the blood. Each filament has thousands of fine branches (lamellae) that are exposed to the
Blood vessels flow blood throughout the body. Arteries transport blood away from the heart. Veins return blood back toward the heart. Capillaries surround body cells and tissues to deliver and absorb oxygen, nutrients, and other substances
Blood is actually a tissue. It is thick because it is made up of a variety of cells, each having a different job. In fact, blood is about 80% water and 20% solid.
Cells are the smallest, structural and functional unit of an organism, which is characteristically microscopic. Tissues are the distinct types of material consisting of specialized cells and their products. Found in both unicellular and multicellular organisms
GILL RACKERS
are bony or cartilaginous serve to protect the gill
How do gills promote gas exchange?
Fish exchange gases by pulling oxygen-rich water through their mouths and pumping it over their gills. In some fish, capillary blood flows in the opposite direction to the water, causing counter-current exchange. The gills push the oxygen-poor water out through openings in the sides of the pharynx
HUMAN LUNGS
Ventilation: The exchange of air between the atmosphere and the lungs – achieved by the physical act of breathing. ... Cell Respiration: The release of energy (ATP) from organic molecules – it is enhanced by the presence of oxygen (aerobic)
Respiratory mechanics refers to the expression of lung function through measures of pressure and flow.
Thoracic cavity, also called chest cavity, the second largest hollow space of the body. It is enclosed by the ribs, the vertebral column, and the sternum, or breastbone, and is separated from the abdominal cavity
Why is the composition of inhaled and exhaled air different?
1 Answer. The inhaled air has larger concentration of oxygen and lesser concentration of carbon dioxide, whereas exhaled air has larger concentration of carbon dioxide and lesser amount of oxygen.
haemoglobin
a red protein responsible for transporting oxygen in the blood of vertebrates. Its molecule comprises four subunits, each containing an iron atom bound to a haem group.
Plasma is the liquid portion of blood. About 55% of our blood is plasma, and the remaining 45% are red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets that are suspended in the plasma. Plasma is about 92% water.
Hemoglobin is a heterotetrameric oxygen transport protein found in red blood cells (erythrocytes), whereas myoglobin is a monomeric protein found mainly in muscle tissue where it serves as an intracellular storage site for oxygen.
Both the molecules have oxygen binding ability, as discussed above, following are the key differences. ... Haemoglobin binds with O2, CO2, CO, NO, BPH and H+, while myoglobin binds with O2 only. It supplies haemoglobin along with blood systemically all over the body while myoglobin supplies oxygen to muscles only
What is the Difference Between Plasma and Blood? Blood is the main body fluid that helps in the transportation of nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and waste products to carry out waste products. Plasma is the liquid component of the blood excluding blood cells. It is composed of Plasma, WBC, RBC, and platelets.
A respiratory pigment is a metalloprotein that serves a variety of important functions, its main being O₂ transport. Other functions performed include O₂ storage, CO₂ transport, and transportation of substances other than respiratory gases.
A respiratory pigment is a molecule, such as hemoglobin in humans, that increases the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood. Examples of respiratory pigments are hemoglobin, haemocyanin, haemerythrin and chlorocruorin.
It because : Plants have special structures on their leaves called as stomata through which they can perform exchanging of the gases. So, they do not require any organ for respiration. ... This is the reason of why plants do not require any kind of respiratory organ.




Comments
Post a Comment