Nutrition
the process of providing or obtaining the food necessary for health and growth.
What is food?
A substance that provides nourishment(lishe)
Autotrophic nutrition
Chlorophyll is found in virtually all Photosynthetic Organisms, including green plants, cyanobacteria(blue-green algae), and algae. It absorbs energy from light; this energy is then used to convert carbon dioxide to carbohydrates. Chlorophyll is a pigment found in green plants.
Pigments or Biochromes, are substances produced by living organisms that have a color resulting from selective color absorption.
Photosynthesis and chemosynthesis are both processes by which organisms produce food; photosynthesis is powered by sunlight while chemosynthesis runs on chemical energy.
If starch not present the color remain yellow or orange
Leaf will change Dark-green
is a process where an organism prepares its own food from a simple inorganic material like water, mineral salts and carbon dioxide in the presence of sunlight.” The term “autotrophic” is formed by the combination of two terms, “auto” meaning self, and “trophic” meaning nutrition.
Obligately Anaerobic are organisms live without oxygen and can be killed by it
Photorelocation is process of chloroplast moving to control light exposure
During photosynthesis Oxygen bubble seen more than carbondioxide due to Carbondiode dissolve in water more than Oxygen
Carbondiode dissolve in water from carobnic acid
MORE:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=c7Ya5xoy2nw
Synthesis
is the production of chemical compounds by reaction from simpler materials.
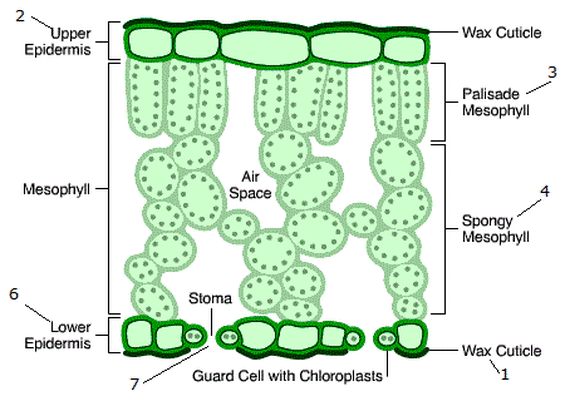
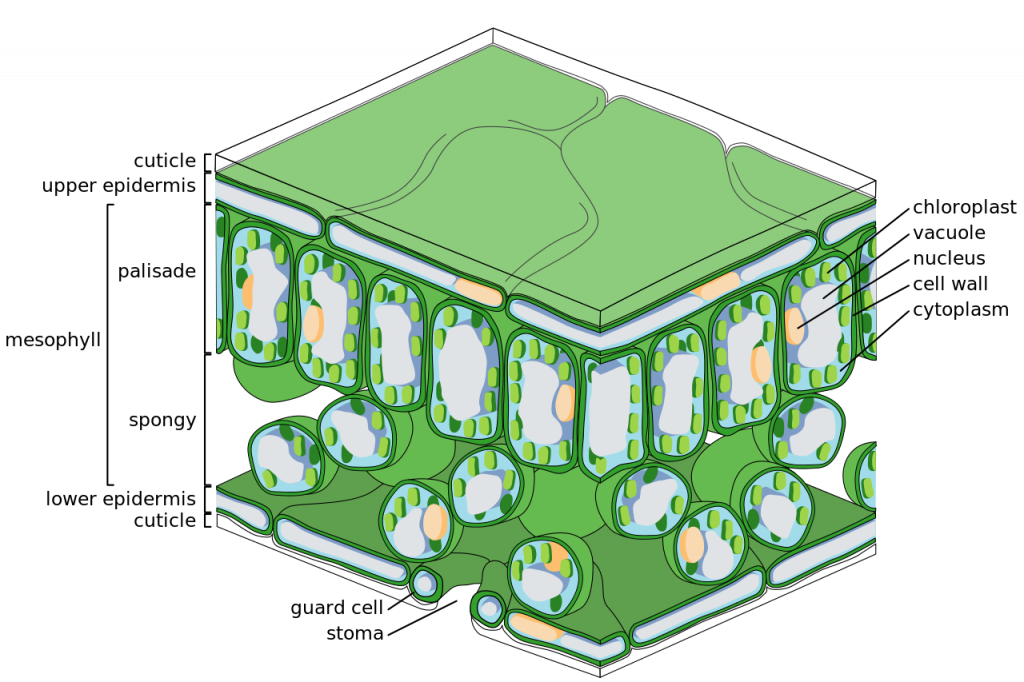
Traverse Section Of Leaf
Starch is high calorie that convert to sugar during digestion
Starch also produced by green plant as energy store
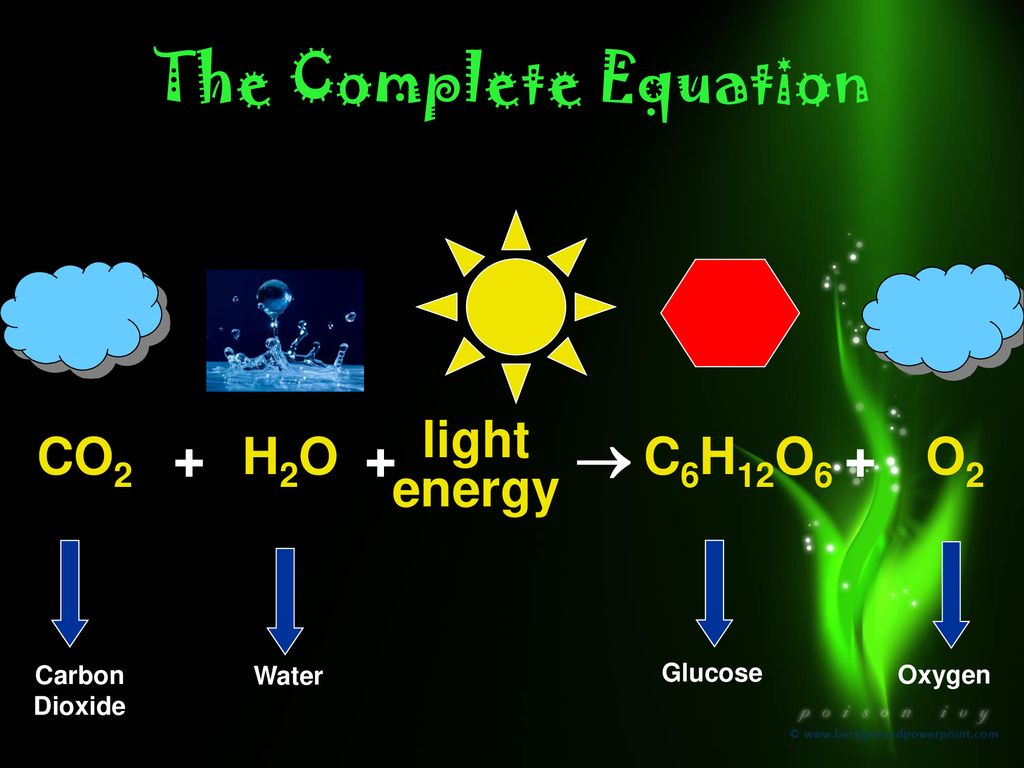
During photosynthesis, plants trap light energy with their leaves. Plants use the energy of the sun to change water and carbon dioxide into a sugar called glucose. Glucose is used by plants for energy and to make other substances like cellulose and starch. Cellulose is used in building cell walls.
Photosynthesis organism change light energy to chemical energy in the presence of water, carbondioxide, sunlight and chlorophyll
Photosynthesis takes place inside cellular organelles called Chloroplast
- which contain abundant chlorophyll pigment
Plants have to produce starch to store energy for cell metabolism. ... When a human eats starchy plant material, some of the starch breaks down into glucose for energy: any unused remnant of this ingested energy is stored as fat deposits.
If there is still excess glucose, it will be converted and stored as body fat. Eating too many calories from sugar or starch can cause weight gain. Also, a diet high in refined starches and added sugars is linked to a higher risk for cardiovascular disease.
The cardiovascular system is sometimes called the blood-vascular, or simply the circulatory, system. It consists of the heart, which is a muscular pumping device, and a closed system of vessels called arteries, veins, and capillaries.
Exercise Burn off more energy(starch in body-fat) is losing weight
Calorie is measure of how much energy
Energy release during digestion and stored in other molecules and can be broken down to produce energy when body need . This energy can be used by body for digestion, physical activity and basic function of organ and tissues
CAlories is show much energy food contain
MORE: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VEQaH4LruUo
Excess glucose(Starch), it will be converted and stored as body fat.
Excess protein consumed is usually stored as fat (Protein can produce more energy than carbohydrate when there is excess oxygen)
Both starch and sugar offer 4 calories
Starch converted to glucose(energy / sugar) by enzymes called Amlyse and assisted with water
Test Presence of Starch in Potato, Rice
ADDING IODINE TO STARCH
Iodine is Yellow-Brown color
Starch food (rice , potato) will be changed to blue-black
In non-starch food color will not change(Yellow-Brown color)
Blue-black is due to formation of Polyiodide chain from reaction of iodine and starch
Adding Iodine to starch change to blue-black
Blue-black is formation of polyiodide chains as reaction of starch and iodine
Iodine have Yellow-Brown color
Test Presence of Starch in Leaf
ADDING IODINE TO LEAF
During Photosynthesis Leaves of Plant produce Glucose.
But remember when its more excess of glucose in plant its store as starch
How to do this experiment:-
- take a leaf plant , and expose on sunlight for several hours
- put leaf in beaker of boiling water - will make cell membrane fine to allow iodine to enter to the cell and react
-Then put leaf in test tube and cover with alcohol
- Put test tube in boiling water beaker
- Chrophyll will dissolve in alchol - alchol turn green - this help to see color change
-Put leaf in petri dish and iodine solution
-Color will changed to Dark-Green
Alcohol is for removing pigment
Boiled Water to make Leaf wall and membrane fine to allow Iodine to penetrate inside the leaf and in order reaction to occur
Test Presence of Oxygen as Product During Photosynthesis
GAS EVOLVED DURING PHOTOSYNTHESIS
LIGHT IS ESSENTIAL FOR PHOTOSYNTHESIS
Starch is stored in the stroma of the chloroplasts and in the cytoplasm of leaves.
Detached Plant : Plant use its own starch stored due to fail of photosynthesitic factor like light, carbondioxide, water
CARBONDIOXIDE IS ESSENTIAL FOR PHOTOSYNTHESIS
CHLOROPHYLL IS ESSENTIAL FOR PHOTOSYNTHESIS
Photolysis is the process where by sunlight broken down water into hydrogen and oxygen
Hydrogen produced during photolysis combine with carbondioxide to form carbohydrates.
Example of hexoses Sugar are glucose, galactose, mannose, and fructose.
Classification of CARBOHYDRATES
hydrolysis the chemical breakdown of a compound due to reaction with water.
Benedict's reagent /Benedict's qualitative solution /Benedict's solution
Is mixture of Sodium carbonate( Na2CO3) , Sodium Citrate(Na3C6H5O7) and copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate(CuSO4.5H2O).
Is mixture of Sodium carbonate( Na2CO3) , Sodium Citrate(Na3C6H5O7) and copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate(CuSO4.5H2O).
Sodium carbonate( Na2CO3) - provide alkaline medium
Sodium Citrate(Na3C6H5O7) - prevent precipitation of cupric ions
copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate(CuSO4.5H2O) - provide cupric ions
The difference between cuprous and cupric is that cuprous is copper 1+ cation whereas cupric is copper +2 cation.
Nutrient. Nutrients are chemical compounds in food that are used by the body to function properly and maintain health. Examples include proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals.
These nutrient classes can be categorized as either macronutrients (needed in relatively large amounts) or micronutrients (needed in smaller quantities). The macronutrients are carbohydrates, fats, fiber, proteins, and water. The micronutrients are minerals and vitamins.
TYPES OF HETEROTROPHIC NUTRITION: https://byjus.com/biology/heterotrophic-nutrition/#:~:text=Heterotrophic%20nutrition%20can%20be%20one,Examples%20include%20bacteria%20and%20fungi.
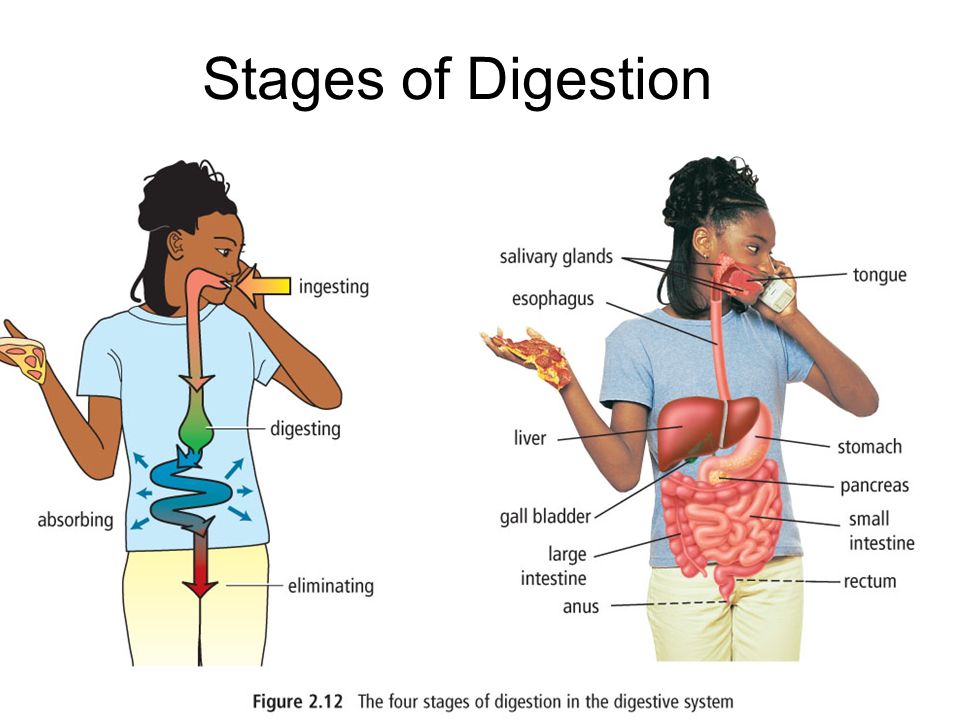
INGESTION
Is the process of taking food, drink, or another substance into the body by swallowing or absorbing it
NON Photosynthetic Plants (Parasitic plants) :- can be holoparasites, with virtually no chlorophyll and thus completely parasitic, or they can be hemiparasites, with the ability to photosynthesize to some degree.
Phagocytosis: The process by which a cell engulfs particles such as bacteria, other microorganisms, aged red blood cells, foreign matter
The fluid inside AMOEBA vacuole contains several enzymes that digest the food and digested parts are absorbed into the cytoplasm. Undigested waste parts are thrown out of the cell.
Symbosis
Is relationship in which one organism can benefit or all species
Example : Clown Fish and Anemone - Mutualistic
Anemone have sting to harm predator but can not Clown Fish becoz of Symbosis. relationship.
Categories Of Symbosis
- Parasitism : Is benefit one organism while other is harm Eg tapeworms, louse, fleas, .
- Mutualism : Is benefit all organisms Eg bee and the flower, spider crab and the algae, The bacteria and the human.
- Commensalism: Is benefit one organism while other not harmed Eg Romera fish and shark, Tree frog and frog
Aneroxia Nervosa is lack or loss of appetite for food (as a medical condition).
Impulse Transmission meaning
is the transmission of a nerve impulse along a neuron from one end to the other occurs as a result of electrical changes across the membrane of the neuron
Homeostasis
is the ability or tendency of the body or a cell to seek and maintain a condition of equilibrium Eg If blood pressure is too high, the heart should slow down
Ruminants Animals: wanyama wasio cheua
Second Class protein or Incomplete protein are vegetable proteins, which are grains, nuts, pulses and seeds. They are classified as incomplete protein because these foods by themselves are low in one or more of the essential amino acids.
The human body uses amino acids to make proteins to help the body: Break down food. Grow. Repair body tissue.
Amphoteric meaning able to react both as a base and as an acid.
Essential Ammino Acid is not synthesis by body so its come with diet
Enzymes is substance produced by organism which act as catalyst
Haemoglobin is red protein responsible for transfering oxygen in blood of vertebrates.
Hormones are chemical substances that act like messenger molecules in the organism
Fibrinogen is a blood plasma protein that's made in the liver.
Tendon is the fibrous connective tissue which attaches muscle to bone.
Ligament is the fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to other bones.
Keratin is the type of protein that makes up your hair, skin, and nails.
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body, found in the bones, muscles, skin, and tendons. It is the substance that holds the body together.
Fibrin (also called Factor Ia) is made from fribrinogen deal with blood clotting
Myosin is protein change chemical energy(ATP) to mecahnical. Found in muscle
Glycogen is substance deposited in bodily tissues as a store of carbohydrates. It is a polysaccharide which forms glucose on hydrolysis. 'Glucagon stimulates conversion of glycogen to glucose for use by the cells as energy.
You eat carbohydrates such as sugars and starches to give you energy. The digestion of carbohydrates by enzyme catalysed hydrolysis begins in your mouth and continues in your stomach and small intestine. The final product of the digestion of carbohydrates are monosaccharides such as glucose and fructose.
Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts help speed up chemical reactions in the human body.
Glucose is a simple sugar or monosaccharide.
Examples Of Enzymes
👉 mean break
Amylase 👉 Starch ➡ Sugar - found in saliva
Maltase 👉 Sugar Maltose ➡ glucose - found in saliva
Lactase 👉 Sugar Lactose, Sugar in milk, ➡ glucose - found in small intestine
Protase 👉 Protein ➡ Ammino acid - found in stomach
Nuclease 👉 Nucleic acid ➡ Nucleotides -
Lipase 👉 Lipids / Fat ➡ fatty acid + glycerol - found in gut
Hydrolysis is chemical reaction where by compound breaking down by using water
Assisted by Enzymes in breaking down
Cellulose (polysaccharide)(fibrous carbohydrates that form structure of plant)is an important structural component of the primary cell wall of green plants, many forms of algae and the oomycetes.
Cellulose/roughage can not be digested , help flowing food through the gut, but bacteria of ruminant animal can digest cellulose
Polymers are broken down into monomers in a process known as hydrolysis, which means “to split water,” a reaction in which a water molecule is used during the breakdown. During these reactions, the polymer is broken into two components.THEN Monomers enter in blood
Monosaccharides can not broken down(small unit)
Oligossacharides is contain more than two monosarcharides but less than 10 monosaccharides
Polyssacharides is contain large number of monossacharides more than ten
Fat-soluble vitamins are vitamins A, D, E, and K. They are present in foods containing fats. The body absorbs these vitamins as it does dietary fats. They do not dissolve in water.
MORE: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/320310#vitamin-a
Water-soluble vitamins are vitamins B, C
Vitamin A
Source:
- - Vegertable and Carrot
- - Milk and egg and oil fish
Function:
- -Vision
- -Skin
Defiency: Blind ness, Dry Skin
Vitamin B1
Source:
- - Fresh Fruit
- - nut and peas
Function:
- -Help body's cell change carbohydrates to energy
- -role in muscle growth
Defiency: Beriberi
Vitamin B2
Source:
- - Milk
- - Egg
Function:
- - Body growth
- - red blood cell production
- cell metabolism
Defiency: Riboflavin deficiency (also known as Ariboflavinosis)
Symptoms: edema of mouth and throat , Skin disorder and mouth crack
Vitamin B3
Source:
- - Fish , pork
- - Chicken Breast, liver
Function:
- - helps turn the food you eat into the energy
Defiency: Indigestion
Vitamin B6
Source:
- - Fish , pork
- - Chicken Breast, liver
Function:
- - help in functtion nerve
- - cell metabolism
- - production of red blood cell
Defiency: nerve pain, weak immune function
Vitamin B12
Source:
- - poultry: chicken, turkey
- - animal: meat
- dairy product
Function:
- - help in make DNA in cell
- - help nerves and red blood cell be healthy
Defiency: nerve pain, weak immune function
A lack of B12 damages the myelin sheath that surrounds and protect nerves. Without this protection, nerves cease to function properly and conditions such as peripheral neuropathy occur.
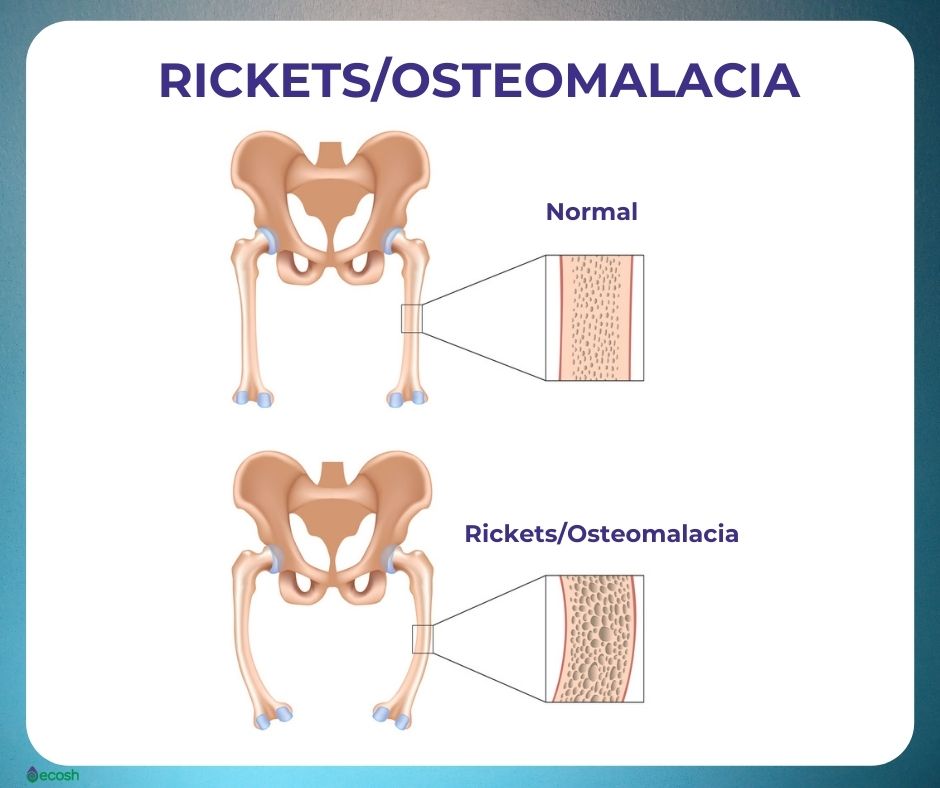
Osteomalacia refers to a marked softening of your bones, most often caused by severe vitamin D deficiency. The softened bones of children and young adults with osteomalacia can lead to bowing during growth, especially in weight-bearing bones of the legs.
Malnutrition is lack of proper nutrition,
caused by not having enough to eat, not eating enough of the right things, or being unable to use the food that one does eat. "nearly 67% of the country's population suffers from malnutrition
Absorption is the release of digested food into the blood stream.
Assimilation is the use of digested food in the organisms cells.
Egestion is the removal of indigestible waste materials from the body.
Benedict's reagent - used to test reducing sugar
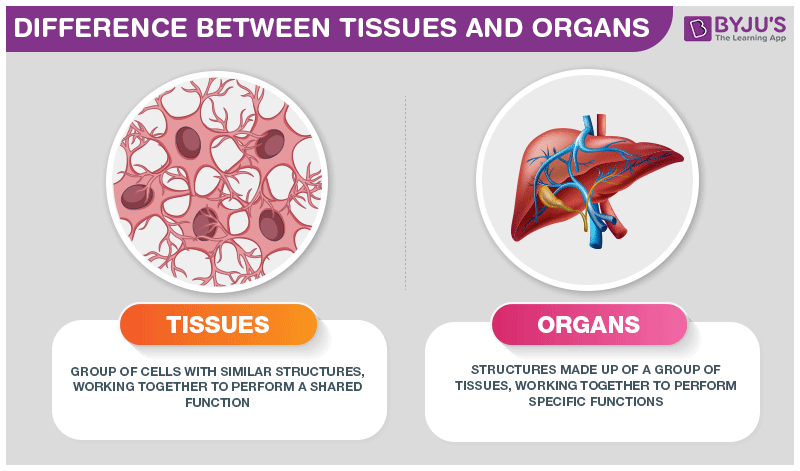
Difference between Tissues And Organ






Comments
Post a Comment