What is Mesophyll Cell?
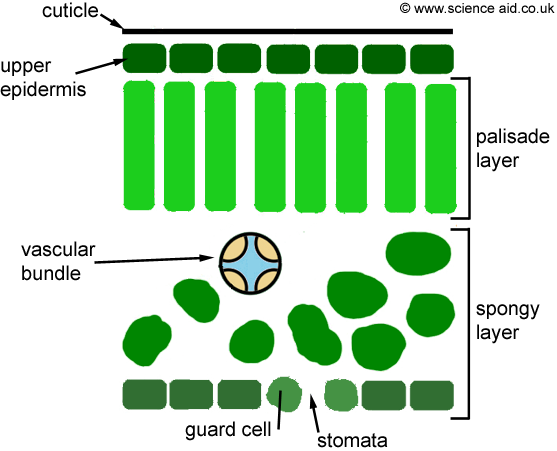
Mesophyll cells are a type of ground tissue found in the plant's leaves. The most important role of the mesophyll cells is in photosynthesis. Mesophyll cells are large spaces within the leaf that allow carbon dioxide to move freely.
Palisade mesophyll cells are tall and closely packed to absorb maximum light. They contain many chloroplasts.
They contain many chloroplasts. Most photosynthesis takes place in the palisade cells
spongy mesophyll's is to allow for the interchange of gases (CO2) that are needed for photosynthesis. within the leaf that allow carbon dioxide to move freely
Transiparation
TRANSPIRATION PULL
a biological process in which the force of pulling is produced inside the xylem tissue.
Cell sap is a fluid found in the vacuoles (small cavities) of the living cell; it contains variable amounts of food and waste materials, inorganic salts, and nitrogenous compounds. ... Phloem, or sieve-tube, sap is the fluid carrying sugar from leaves to other parts of the plant in the summer.
How does cell sap help in osmosis?
The rate of transpiration is affected by several factors, including:
- temperature.
- humidity.
- wind speed.
- light intensity.
Turgor, Pressure exerted by fluid in a cell that presses the cell membrane against the cell wall. Turgor is what makes living plant tissue rigid. Loss of turgor, resulting from the loss of water from plant cells, causes flowers and leaves to wilt.
Protoplasm, the cytoplasm and nucleus of a cell. The term was first defined in 1835 as the ground substance of living material and, hence, responsible for all living processes. Advocates of the protoplasm concept implied that cells were either fragments or containers of protoplasm.
Plant species with adaptations that allow it to survive in hot temperatures are called xerophytic



Comments
Post a Comment